Registration algorithms
4 registration methods are offered within the application: StackReg, SIFT, a combined approach (SIFT + StackReg), and a User-driven one
StackReg
This algorithm is based on a minimization processing based on cross-correlation of binarized images of similar size. Binarization and image resizing are handled automatically within the code. Binarization is performed to achieve, by default and as closely as possible, a 50-50 distribution of True-False (or 0-1) values for the selected regions (either ROIs or entire images). In some cases, users have to adjust this threshold in the Options tab to better highlight features essential for accurate alignment.
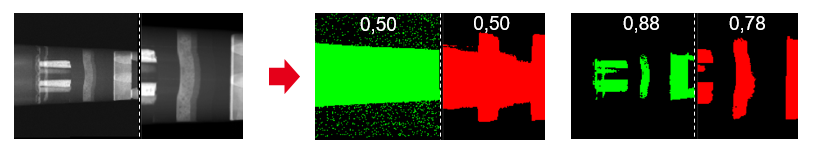
Illustration of adjusting the Threshold in the Options tab to reveal features.
It is important to note that StackReg relies on a gradient descent method to minimize misalignment. Therefore, it requires the images to already have significant overlap in their features to function effectively.
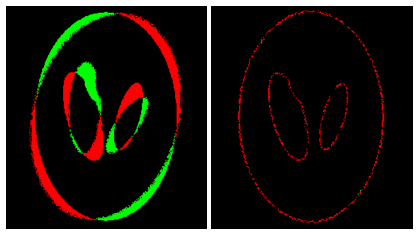
Illustration of overlapping patterns required for a correct alignment with the StackReg algorithm. (left) before registration (right) after.
SIFT
This method, named SIFT for Scale-Invariant Feature Transform, identifies and matches key features between the two images to align them. Unlike StakReg, SIFT does not require binarization or rescaling of the images. However, the images must contain distinct, recognizable features for successful alignment.
Due to the random sampling process used to match features between images, consecutive executions of this algorithm may yield slightly different results.
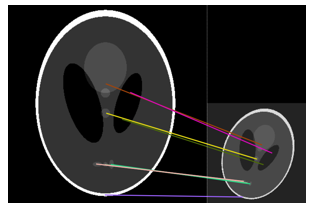
Illustration of the SIFT algorithm application with representation of the matching points (limited to the 10 first) in the Juxtaposed images view.
SIFT + StackReg
This combined approach leverages the strengths of both methods. SIFT first performs a primary alignment, bringing potentially highly misaligned images closer together. Then, StackReg refines this alignment to achieve possibily a higher level of precision.
User-Driven
This method allows users to manually define matching points between the two juxtaposed images using the mouse. Users can add pairs of points with left-click and remove the nearest existing pair with a right-click.