Destriping
The destriping process step aims at minimizing artefacts like stripes or curtaining effects that can appear in some image acquisition technics (typically FIB-SEM).
The main algorithm used for the destriping is issued from the pyvnsr library. A second algorithm based on wavelet decomposition (from Münch B. et al.) is also available and may be suitable for fast removal of vertical stripes.
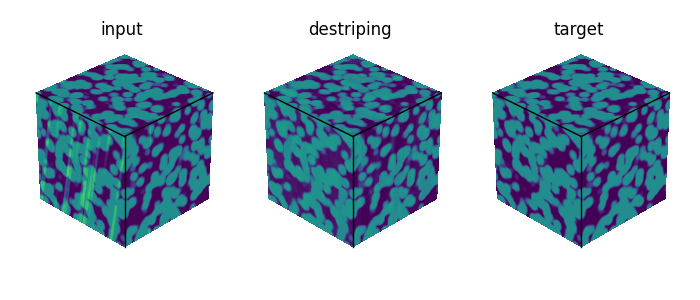

Illustration of the destriping process step in the synthetic test case.
[destriping]
maxit = 50
cvg_threshold = 1e-2
filters = [{ name = "Gabor", noise_level = 200, sigma = [2, 80], theta = 10 }]
maxit refers to the number of iterations used by the pyvnsr algorithm.
cvg_threshold is a convergence criterion that can be used to stop the iterative pyvnsr process when the maximum residual variation between 2 iterations has reached this value.
filters consists of a list of filters to be used during the destriping process and are related to the shape and intensity of the stripes to be removed.
For each of these parameters, see the pyvnsr documentation for more details.
In the frame of wavelet decomposition:
[destriping]
wavelet_decomposition = {'wavelet':'coif3', 'level':4, 'sigma':4}
wavelet and level refer respectively to the wavelet name family to use (see pywt.wavelist) and the level of decomposition.
sigma is related to the standard deviation to be considered in the gaussian filter applied during the wavelet decomposition.